High Speed Multilayer Printed Circuit Board Layer-Up Structure Design
The main factors considered in the High Speed Multilayer Printed Circuit Board Layer-Up Structure Design are the heat resistance of the material, the withstand voltage, the amount of glue filling and the thickness of the dielectric layer, etc. The following main principles should be followed:
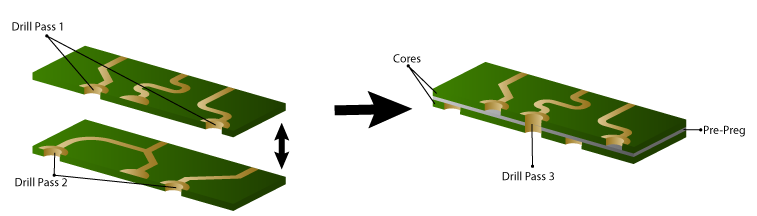
(1) Prepreg and core board manufacturers must be consistent. In order to ensure the reliability of PCB, all layers of prepreg should avoid using single 1080 or 106 prepreg (except customers have special requirements). If the customer has no dielectric thickness requirements, the thickness of the dielectric between each layer must be guaranteed according to IPC-A-600G ≥ 0.09mm.
(2) When the customer requires high TG sheet, the core board and the prepreg must use the corresponding high TG material.
(3) The inner layer substrate is 3.0OZ or above, and the prepreg with high resin content is selected, such as 1080R/C65%, 1080HR/C 68%, 106R/C 73%, 106HR/C76%; However, when cloning multilayer pcb board stack up structure, try to avoid the structural design of using all 106 high glue prepregs to prevent multiple 106 prepregs from overlapping. Because the glass fiber yarn is too thin, the glass fiber yarn collapses in the large base material area, which affects the dimensional stability and explosion board delamination.
(4) If the customer has no special requirements, the thickness tolerance of the interlayer dielectric layer is generally controlled by +/-10%. For the impedance plate, the dielectric thickness tolerance is controlled by the IPC-4101 C/M class tolerance. If the impedance influencing factor is related to the thickness of the substrate If relevant, the sheet tolerances must also be in accordance with IPC-4101 Class C/M tolerances.
Tags: Clon de placa de circuito impreso multicapa de alta velocidad,Copia de placa de circuito impreso multicapa de alta velocidad,Ingeniería inversa de placa de circuito impreso multicapa de alta velocidad,Réplica de placa de circuito impreso multicapa de alta velocidad

