Automotive Radar PCB Board Cloning
Many high-performance automotive assistance systems rely on radar to gather information about the vehicle’s surroundings. Their usefulness is that they can accurately calculate the distance and relative speed between the vehicle and the preceding vehicle based on the principle of reflected waves and Automotive Radar PCB Board Cloning is playing an important role in it.
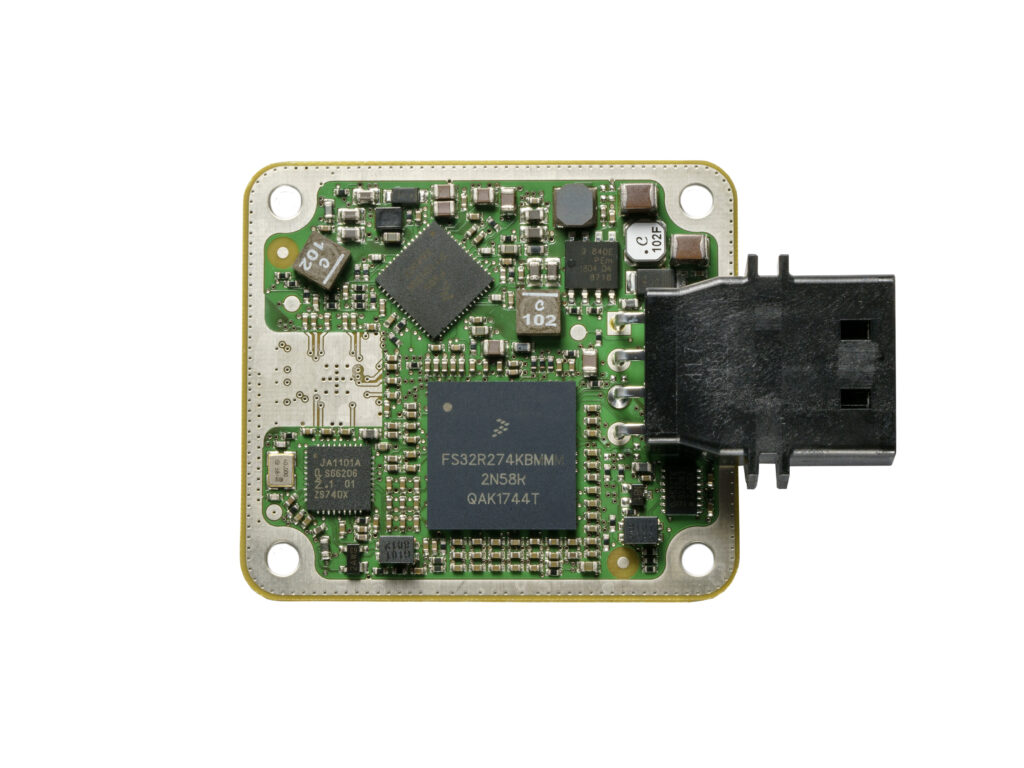
Bosch’s fourth-generation long-range radar sensor PCB board circuitry pattern (Long-Range Radar, LRR4) was re on the basis of the development and production experience of the third-generation radar. The LRR4 is the same as the previous generation, using the 77 GHz band and having no moving parts.
All components are fixedly installed in various parts of the vehicle, which improves the stability of the system. The LRR4 radar sensor integrates two electronic pc boards which can be used for copying, including microcontrollers from NXP and STMicroelectronics which need to be reverse engineered for its memory program and data, and a power management IC from Bosch. The radio frequency (RF) pcb circuit board cloning technology adopts an asymmetric structure based on a hybrid PTFE/FR4 substrate with a planar antenna mounted.
Among them, Infineon’s 77 GHz silicon germanium (SiGe) monolithic microwave integrated circuits (MMICs) are used as high-frequency transmitters and receivers.
The LRR4 comes from Bosch and is a multi-mode radar with six fixed radar antennas. Four centrally arranged antennas provide high-speed recording of the environment, creating a focused beam with an aperture angle of ±6° with minimal disturbance to traffic in adjacent lanes. For near-field situations, the LRR4’s two external antennas can expand the field of view to ±20° with a range of 5m, enabling fast detection of vehicles entering or leaving the lane

