Printed Circuit Board Composition
The basic aspects of Printed Circuit Board Composition include dielectric materials, copper and trace sizes, and mechanical layers or size layers. The material used as the dielectric provides two basic functions for the PCB.
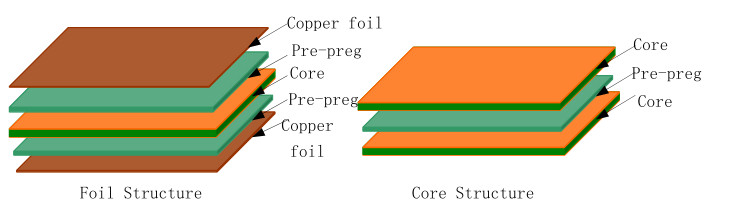
When we build complex PCBs that can handle high-speed signals, dielectric materials isolate the signals found on adjacent layers of the PCB. The stability of the PCB depends on the uniform impedance of the dielectric on the entire plane and the uniform impedance over a wide frequency range.
Although it appears that copper is obvious as a conductor, there are other functions. Different weights and thicknesses of copper will affect the ability of the circuit to achieve the correct amount of current and define the amount of loss.

As far as the ground plane and the power plane are concerned, the quality of the copper layer will affect the impedance of the ground plane and the thermal conductivity of the power plane.
Matching the thickness and length of the differential signal pair can consolidate the stability and integrity of the circuit, especially for high-frequency signals.

