Dynamic Circuit Board Effects
Although static circuit board effects can come and go with changes in humidity or board contamination, problems that most noticeably affect the Dynamic Circuit Board Effects usually remain relatively constant. Short of a new design, washing or any other simple fixes can’t fix them. As such, they can permanently and adversely affect a design’s specifications and performance.
The problems of stray capacitance, linked to lead and component placement, are reasonably well known to most Circuit Board designers. Since lead placement can be permanently dealt with by correct layout, any remaining difficulty is solved by training assembly personnel to orient components or bend leads optimally.
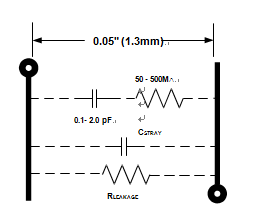
Dielectric absorption (DA), on the other hand, represents a more troublesome and still poorly understood circuit-board phenomenon. Like DA in discrete capacitors, DA in a printed-circuit board can be modeled by a series resistor and capacitor connecting two closely spaced nodes. Its effect is inverse with spacing and linear with length.
As shown in below Figure, the RC model for this effective capacitance ranges from 0.1 pF to 2.0 pF, with the resistance ranging from 50 M to 500 M. Values of 0.5 pF and 100 M are most common. Consequently, circuit-board DA interacts most strongly with high impedance circuits.